Chúng ta thường nhầm tưởng quá trình xây dựng phần mềm (software construction) chủ yếu là lập trình(coding) và sửa lỗi (debugging). Tuy nhiên, quá trình này trải rất nhiều hoạt động:
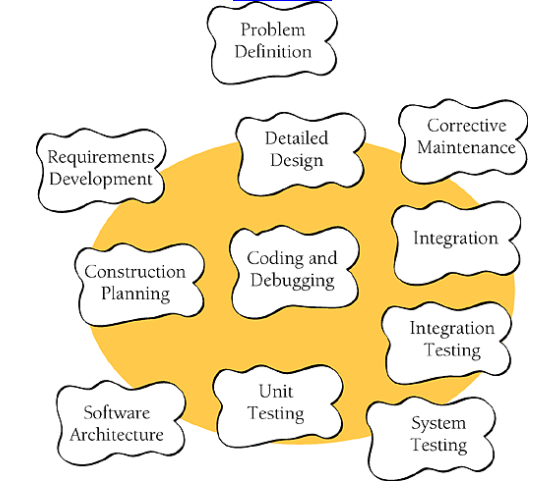
Các hoạt động chính trên vòng tròn, hoạt động Problem Definition tuy bên ngoài vòng tròn nhưng cũng rất quan trọng vì đây là giai đoạn chúng ta hình thành bức tranh về phần mềm cần xây dựng.
Tùy theo dự án, quá trình software construction chiếm 30-80 % thời gian xây dựng dự án. Là hoạt động trung tâm của phát triển phần mềm.
Việc xây dựng phần mềm phải đối mặt với nhiều rủi ro nên cần có chuẩn bị kỹ lưỡng trong giai đoạn tiền dự án. Giai đoạn này, thường bị bỏ qua hay làm rất qua loa, có ảnh hưởng rất lớn đến chất lượng của toàn bộ dự án.
Tùy theo kiểu dự án mà chúng ta tiếp cận theo kiểu tuần tự (sequential approach) hay kiểu lặp (iterative approach). Dù cách tiếp cận nào thì giai đoạn tiền dự án cũng phải đảm bảo các vấn đề sau:
Thứ nhất là phân tích các yêu cầu của dự án (requirements) như yêu cầu về chức năng, chất lượng, hay tiêu chuẩn hoàn thành dự án. Sau đây là bộ checklist tập hợp các câu hỏi dùng trong giai đoạn phân tích các yêu cầu của dự án.
Checklist: Requirements
Specific Functional Requirements
- Are all the inputs to the system specified, including their source, accuracy, range of values, and frequency?
- Are all the outputs from the system specified, including their destination, accuracy, range of values, frequency, and format?
- Are all output formats specified for Web pages, reports, and so on?
- Are all the external hardware and software interfaces specified?
- Are all the external communication interfaces specified, including handshaking, error-checking, and communication protocols?
- Are all the tasks the user wants to perform specified?
- Is the data used in each task and the data resulting from each task specified?
Specific Nonfunctional (Quality) Requirements
- Is the expected response time, from the user’s point of view, specified for all necessary operations?
- Are other timing considerations specified, such as processing time, data transfer rate, and system throughput?
- Is the level of security specified?
- Is the reliability specified, including the consequences of software failure, the vital information that needs to be protected from failure, and the strategy for error detection and recovery?
- Are minimum machine memory and free disk space specified?
- Is the maintainability of the system specified, including its ability to adapt to changes in specific functionality, changes in the operating environment, and changes in its interfaces with other software?
- Is the definition of success included? Of failure?
Requirements Quality
- Are the requirements written in the user’s language? Do the users think so?
- Does each requirement avoid conflicts with other requirements?
- Are acceptable trade offs between competing attributes specified—for example, between robustness and correctness?
- Do the requirements avoid specifying the design?
- Are the requirements at a fairly consistent level of detail? Should any requirement be specified in more detail? Should any requirement be specified in less detail?
- Are the requirements clear enough to be turned over to an independent group for construction and still be understood? Do the developers think so?
- Is each item relevant to the problem and its solution? Can each item be traced to its origin in the problem environment?
- Is each requirement testable? Will it be possible for independent testing to determine whether each requirement has been satisfied?
- Are all possible changes to the requirements specified, including the likelihood of each change?
Requirements Completeness
- Where information isn’t available before development begins, are the areas of incompleteness specified?
- Are the requirements complete in the sense that if the product satisfies every requirement, it will be acceptable?
- Are you comfortable with all the requirements? Have you eliminated requirements that are impossible to implement and included just to appease your customer or your boss?
Thứ hai là phác thảo kiến trúc hay bức tranh tổng thể của dự án có vai trò quan trọng giúp các nhà phát triển có thể xây dựng dự án thành công. Bộ checklist sau tập hợp các câu hỏi giúp chúng ta định hình kiến trúc dự án một cách hiệu quả:
Checklist: Architecture
Specific Architectural Topics
- Is the overall organization of the program clear, including a good architectural overview and justification?
- Are major building blocks well defined, including their areas of responsibility and their interfaces to other building blocks?
- Are all the functions listed in the requirements covered sensibly, by neither too many nor too few building blocks?
- Are the most critical classes described and justified?
- Is the data design described and justified?
- Is the database organization and content specified?
- Are all key business rules identified and their impact on the system described?
- Is a strategy for the user interface design described?
- Is the user interface modularized so that changes in it won’t affect the rest of the program?
- Is a strategy for handling I/O described and justified?
- Are resource-use estimates and a strategy for resource management described and justified for scarce resources like threads, database connections, handles, network bandwidth, and so on?
- Are the architecture’s security requirements described?
- Does the architecture set space and speed budgets for each class, subsystem, or functionality area?
- Does the architecture describe how scalability will be achieved?
- Does the architecture address interoperability?
- Is a strategy for internationalization/localization described?
- Is a coherent error-handling strategy provided?
- Is the approach to fault tolerance defined (if any is needed)?
- Has technical feasibility of all parts of the system been established?
- Is an approach to overengineering specified?
- Are necessary buy-vs.-build decisions included?
- Does the architecture describe how reused code will be made to conform to other architectural objectives?
- Is the architecture designed to accommodate likely changes?
General Architectural Quality
- Does the architecture account for all the requirements?
- Is any part overarchitected or underarchitected? Are expectations in this area set out explicitly?
- Does the whole architecture hang together conceptually?
- Is the top-level design independent of the machine and language that will be used to implement it?
- Are the motivations for all major decisions provided?
- Are you, as a programmer who will implement the system, comfortable with the architecture?
Cuối cùng trong giai đoạn tiền dự án là tổng hợp, đánh giá từ quá trình phân tích các yêu cầu và phác thảo kiến trúc dự án. Bộ checklist chứa tập các câu hỏi sau đây sẽ giúp chúng ta có bao quát toàn bộ giai đoạn tiền dự án.
Checklist: Upstream Prerequisites
- Have you identified the kind of software project you’re working on and tailored your approach appropriately?
- Are the requirements sufficiently well defined and stable enough to begin construction? (See the requirements checklist for details.)
- Is the architecture sufficiently well defined to begin construction? (See the architecture checklist for details.)
- Have other risks unique to your particular project been addressed, such that construction is not exposed to more risk than necessary?

Ý kiến bài viết